An MPV stands for Mean platelet volume (MPV) in blood tests. It is defined as the average volume or size of platelets. It is measured in femtoliters (fL). Platelet count (PLT) measurement differs from mean platelet volume (MPV).
The platelet count (PLT) is the number of platelets per microL of blood, also expressed as the number of platelets x 10 /L.
Introduction
Human blood has major components like white blood cells (WBCs), red blood cells (RBCs), and platelets. All these hematological components are assessed by complete blood cell count (CBC), the most commonly ordered hematological blood test. MPV is an abbreviated form of mean platelet volume and is also analyzed through CBC blood tests.
Platelets, also called thrombocytes, are the smallest of blood cells, without a nucleus, having a critical role in hemostasis. These survive for 8-10 days and are sequestered by the spleen. Platelets stick together and stop bleeding after the injury.
Platelet production occurs in the bone marrow by megakaryocytes and is released into the bloodstream. Platelet size reflects platelet activity and is a useful predictive and prognostic biomarker in medical conditions.
What is an MPV blood test?
The mean platelet volume, also known as MPV, is a precise measure of their dimension calculated by the blood analyzers on a volume distribution basis. It is an essential part of routine blood morphology tests. In physiological conditions, MPV is inversely proportional to the platelet count; increased platelet production is associated with reduced mean volume.
High MPV means the patient has active bone marrow production and platelets are larger than average. And low MPV means there is bone marrow suppression, and platelets are smaller than normal platelets.
What is the MPV blood test used for?
MPV blood test, a short form for mean platelet volume, is used for diagnosing various blood disorders and other medical conditions. MPV blood test is significant when a patient is symptomatic, or the complete blood count is remarkable.
The first step should be to confirm that the MPV blood test is accurate and the blood was tested within six hours. It is more feasible if the patient has blood drawn in or near the hematology lab.
How to perform an MPV blood test?
Mean platelets volume (MPV) is detected by complete blood cell count (CBC).
Step 1: Phlebotomist (technician who draws blood) will assess your arms to locate a site for blood collection
Step 2: He will locate a prominent vein and will wrap a tourniquet to make it more prominent
Step 3: Then, he will sanitize a spot and will insert a thin needle into your vein
Step 4: He will draw a blood sample into a test tube/vial containing anticoagulants. This sample is stored.
Step 5: He will apply some pressure when he pricks.
Step 6: An automatic hematological analyzer will be used to process the sample
Step 7: An automated report will be handed over to you
What causes high MPV in blood tests?
High MPV is called macro-thrombocytes. Increased MPV means the production or destruction of platelets is very high. It’s higher than the normal range and is usually observed in the following conditions.
- Hyposplenic states because there is no spleen to sequester the more giant platelets
- Cerebral stroke
- ITP, immune thrombocytopenia
- Cardiovascular diseases
- Respiratory diseases
- Intestine diseases
- Rheumatoid diseases
- Chronic renal failure
- Diabetes
- Cancers of various types
What causes low MPV in blood tests?
Low MPV is called micro-thrombocytes. Decreased MPV means it’s lower than the normal range and is usually observed in the following conditions.
- Tuberculosis
- Systemic lupus erythematosus
- Ulcerative colitis
- Cancers of various types
- Autoimmune diseases
- Aplastic anemia
Clinical uses of MPV
Mean platelet volume (MPV) blood test is cheap, rapid, and readily available as part of the routine complete blood count (CBC). Many clinical studies have shown that changes in mean platelet volume (MPV) blood levels are associated with various pathological and inflammatory conditions. Some of these are mentioned in the following text.
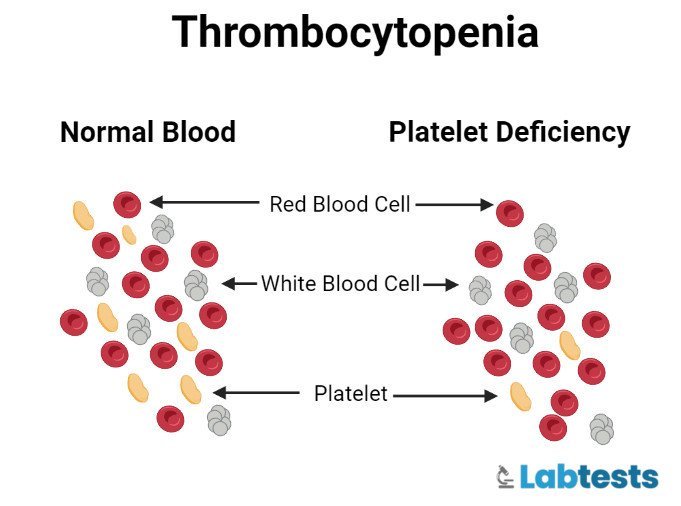
- Thrombocytopenia: MPV is used to distinguish thrombocytopenias due to platelet destruction or bone marrow failure.
- Thrombocytosis: MPV and platelet count are high in myelodysplastic or myeloproliferative conditions.
- Congenital platelet disorders: Congenital anomalies like the May-Hagglin anomaly, The Frechtner-Sebastiani syndromes, and Bernard-Soulier disease can be diagnosed with MPV.
- Sepsis: MPV usually rises in sepsis.
- Thyroid disease: MPV decreases when there is a reduction in thyroid hormone due to thyroid disease.
- Splenectomy: Both MPV and platelet count increase after splenectomy.
- Exercise: Both MPV and platelet count increase after exercise.
- Anemia: MPV increases iron deficiency anemia, thalassemia, and sickle cell disease
- Myocardial infarction: MPV increases in MI.
- Cerebral infarction: MPV increases and platelet count decreases in cerebral infarction.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1. What is the MPV blood test’s average range?
The usual range of MPV is between 7.5 and 12 fl.
Q2. What is the normal MPV blood test result?
MPV blood test has clinical significance and may be normal or abnormal in many conditions. It may be normal (if it is in the reference range) or abnormal (high/low). Different labs have different cutoff points, called reference ranges, for normal high or low results. Generally, the MPV blood test is declared as normal if it’s between 7.5 and 12 fl.
Q3. What is a high MPV blood test result?
MPV blood test will be declared as high if it is more than the cutoff point or reference range mentioned by the lab. If a lab’s normal range is between 7.5 and 12 fl then more than 12 fl will be interpreted as a high MPV blood test.
Q 4. What is a low MPV blood test result?
MPV blood test will be declared as low if it is less than the cutoff point or reference range mentioned by the lab. If a lab’s normal range is between 7.5 and 12 fl then less than 7.5 fl will be interpreted as a low MPV blood test.
Q5. Which factors affect MPV blood test values?
The following factors may affect MPV blood test values
• High blood pressure
• Smoking
• The increased blood glucose level
• Altitude
• Exercise
• Menstruation
• Oral contraceptives
Q6. What is the role of the MPV blood test in pregnancy?
The mean platelet volume (MPV) blood test is significant in pregnancies. Clinical trials have concluded that increasing MPV levels reflects the severe inflammatory process. MPV level increases in pregnancies.
Q7. When should I get an MPV test?
A mean platelet volume blood test is a part of routine investigations. Although, sometimes, it’s explicitly advised due to symptoms that require immediate testing. Some of these symptoms are:
• Uncontrolled bleeding from minor cuts
• Bleeding disorder history
• Regular nose bleeds, also called epistaxis
References
- Gregory A. Threatte, Usefulness of the Mean Platelet Volume, Clinics in Laboratory Medicine, Volume 13, Issue 4, 1993, Pages 937-950, ISSN 0272-2712, https://doi.org/10.1016/S0272-2712(18)30418-9.
- Altınbas S, Toğrul C, Orhan A, Yücel M, Danısman N. Increased MPV is not a significant predictor for preeclampsia during pregnancy. J Clin Lab Anal. 2012 Sep;26(5):403-6. doi: 10.1002/jcla.21542. PMID: 23001987; PMCID: PMC6807353.
- Korniluk, Aleksandra & Koper-Lenkiewicz, Olga & Kamińska, Joanna & Kemona, Halina & Dymicka-Piekarska, Violetta. (2019). Mean Platelet Volume (MPV): New Perspectives for an Old Marker in the Course and Prognosis of Inflammatory Conditions. Mediators of Inflammation. 2019. 1-14. 10.1155/2019/9213074.
- Vélez Paez, Jorge Luis & Legua, Pedro & Páez, Pablo & Irigoyen, Estefanía & Andrade, Henry & Jara, Andrea & López, Fernanda & Pérez Galarza, Jorge & Baldeon, Lucy. (2022). Mean platelet volume and mean platelet volume to platelet count ratio are predictors of sepsis’s severity and mortality. PLOS ONE. 17. e0262356. 10.1371/journal.pone.0262356.